Shining the Light on Vitamin D
Wondering about all the hype around vitamin D? Vitamin D intake has become a major public health concern across the globe, particularly in relation to COVID-19.
Just today, however, a study came out indicating that vitamin D does not improve COVID-19 outcomes. The study, published in the Journal of American Medical Association, is the largest of its kind to date. “The findings do not support the use of a high dose of vitamin D3 for treatment of moderate to severe COVID-19,” the researchers write. Also, today, The Lancet medical journal pulled a preliminary paper from its website that had suggested vitamin D did offer a benefit, citing concerns over the research.
Nevertheless, and while perhaps disappointing in relation to COVID-19, vitamin D deserves its place in the limelight (or sunshine).
The fascination with vitamin D supplementation began with the discovery in the early 1920s that vitamin D prevents rickets—a bone disease common in children in developing countries. Rickets has been mostly eliminated in developed countries because of the fortification of some foods with Vitamin D.
Research suggests that vitamin D may help prevent a variety of illnesses, such as depression, diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and more.
What is Vitamin D?
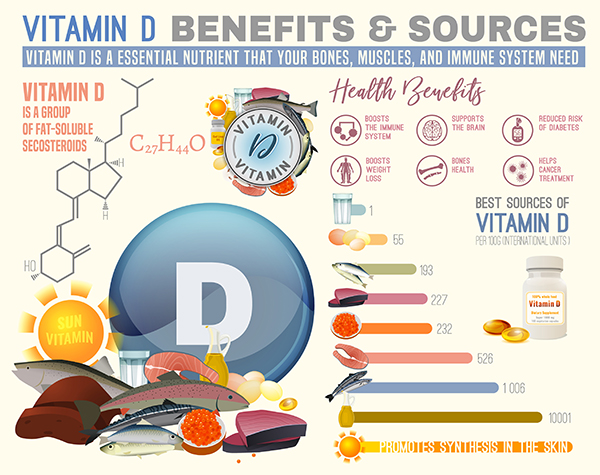
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that primarily aids calcium absorption, promoting growth and mineralization of your bones. It’s also involved in vital processes of your immune, digestive, circulatory, and nervous systems.
Vitamin D is often referred to as “the sunshine vitamin” because the sun is one of the best sources of this essential nutrient. Your skin hosts a type of cholesterol that functions as a precursor to vitamin D. When this compound is exposed to UV-B radiation from the sun, it becomes vitamin D. In fact, sun-derived vitamin D may circulate for twice as long as vitamin D from food or supplements.
Benefits of Vitamin D
Every single cell in your body has a receptor for vitamin D. It works like a hormone and helps with the regulation of genes and improving immunity.
As mentioned above, sunshine on your skin triggers the production of vitamin D in your body.
Also, exposure to sunlight is thought to increase the brain's release of a hormone called serotonin—boosting your mood!
A few more benefits of vitamin D:
• promotes healthy bones and teeth
• supports immune, brain, and nervous system health
• regulates insulin levels and supports diabetes management
• supports lung function and cardiovascular health
• influences the expression of genes involved in cancer development

What Happens if You Don't Produce Enough?
Vitamin D Deficiency (VDD) affects nearly 50% of the population worldwide! All ethnicities and age groups are susceptible to VDD and it is primarily attributed to lifestyle and environmental factors that reduce exposure to sunlight.
You might be at risk of low vitamin D in your body if one or more of these variables apply to you:
- Naturally dark skin: People with darker skin need to spend more time in the sun to produce vitamin D because increased melanin can inhibit vitamin D production.
- Being elderly: As you get older, vitamin D production in your skin becomes less efficient.
- Geographical location and season: adequate sun exposure decreases during the winter months as well as for people living farther away from the equator with less proximity to the sun’s rays.
- Sunscreen and clothing: Certain fabrics and sunscreen can hinder or block sunshine inhibiting vitamin D production.
- Staying indoors: Insufficient time spent outdoors reduces your opportunity for sunshine on your skin to trigger vitamin D production.
- Medications: Certain medications impair vitamin D absorption, including laxatives, steroids, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and some seizure medications.
VDD Can Negatively Impact Your Quality of Life
While the symptoms indicating a vitamin D deficiency may be subtle at first, the ramifications of VDD can be significant.
- Getting Sick or Infected Often: Several large observational studies have shown a link between a deficiency and respiratory tract infections like colds, bronchitis, pneumonia, and now COVID-19.
- Fatigue: Excessive tiredness may be a sign of vitamin D deficiency.
- Bone and Back Pain: Low blood levels of vitamin D may be a cause or contributing factor to bone pain and lower back pain.
- Mood Changes: Depression is associated with low vitamin D levels and some studies have found that supplementing improves mood.
- Impaired Wound Healing: Slow healing of wounds may be a sign that your vitamin D levels are too low. It’s also been suggested that vitamin D’s role in controlling inflammation and fighting infection is important for proper healing.
- Low Bone Mineral Density: Getting enough of this vitamin is important for preserving bone mass as you get older.
- Chronic pain: This link may be due to the interaction between the vitamin and pain-sensing nociceptors. A few studies have found that taking high-dose vitamin D supplements may reduce various types of pain in people who are deficient.
Ways to Increase Your Vit. D Levels & Ensure Absorption
Get some direct sunlight: This is the most straightforward and powerful way to support healthy vitamin D levels. Shoot for 20 minutes per day.
Eat Foods That Contain Vitamin D: Adding mushrooms, healthy fish and protein to your diet is the perfect way to supplement sunlight exposure.
Add a Vitamin D supplement: For many people, a supplement may be the best way to ensure adequate intake beyond sunlight and diet. The scientific community debates how much vitamin D your body needs. Recommendations range from 600 to 2,000 IU of daily vitamin D.
Important note: It’s ideal to have your vitamin D levels tested by your medical professional prior to starting a supplement to ensure you’re taking the most appropriate dose.
Light Therapy: Some people don’t have the luxury to bask in the sun. UV lamps mimic the action of the sun and can be especially helpful if your sun exposure is limited due to geography or time indoors. Read more about Seasonal Affect Disorder.
- Eat enough calcium. Vitamin D and calcium work together to make your bones strong. Make sure you get enough calcium by including a selection of dairy products, leafy vegetables, fish, tofu, Brazil nuts and almonds in your diet.
- Take supplements with the major meal of the day. The timing of taking these supplements matters for better absorption. Taking it with something light impedes absorption.
- In tandem with other vitamins. “For better absorption of vitamin D, you must include vitamin K, A, magnesium, and zinc in your diet. They speed up the absorption procedure,” suggests Amreen Shaikh, head dietician and nutritionist at Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai.
- Eat enough fat. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble nutrient, it needs healthy fat for vitamin D to penetrate deep in the body. According to Ms Shaikh, ghee or oil taken in moderation will never harm you.

Further reading and sources:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/how-to-increase-vitamin-d
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/ten-tips/10-tips-for-getting-enough-vitamin-d
Stay connected for free resources to expand your health and vitality with non-allopathic remedies and natural CBD solutions.
