Celiac Disease Awareness: Facts, Symptoms, and the ECS
Celiac disease (CD) is a genetic autoimmune disorder in which a person can’t consume gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye and barley. When someone with celiac disease consumes gluten, their immune system responds by attacking the small intestine, damaging the villi, and inhibiting the absorption of important nutrients. Left undiagnosed or untreated, celiac disease can lead to other disorders.
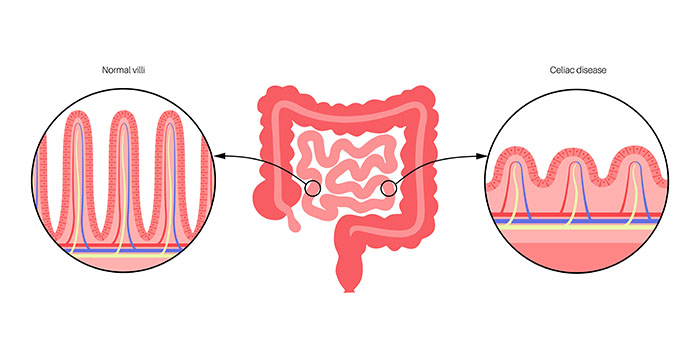
Small intestine cross section, microvilli and epithelial cells.
It’s important to note that gluten sensitivity and celiac disease are different. People with gluten sensitivity may experience bloating and diarrhea — but only people with CD have compromised immune systems as a result of this disease. The only way to truly alleviate celiac disease is by avoiding gluten altogether. However, it can take up to two years for one’s digestive system to heal after starting a gluten-free diet. During this time, patients may still experience some celiac disease symptoms.
When people with CD eat gluten, their body mounts an immune response that attacks the small intestine. This damage to the small intestine can cause a host of problems, including nutrient malabsorption, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue. Some people with celiac disease also suffer from anemia, bone loss, and infertility. CD is often diagnosed in childhood, but it can develop at any age.
There is no cure for CD, but the good news is that a strict gluten-free diet can control symptoms and allow people with celiac disease to lead healthy, normal lives.
The Endocannabinoid System & Celiac Disease
The endocannabinoid system is a network of receptors and neurotransmitters that are responsible for regulating many different bodily functions, including appetite, mood, pain, and inflammation. Celiac disease has been found to be associated with abnormalities in the endocannabinoid system.
In a recent study, it was found that people with CD have lower levels of anandamide, a cannabinoid neurotransmitter, in their blood. Anandamide is known as the “bliss molecule” because it is responsible for producing feelings of happiness and well-being.
The ECS is present in the majority of tissues, including the digestive system. In fact, the intestines contain a very high concentration of endocannabinoids. One of their primary roles here is controlling inflammation.
A 2013 study in PLoS One found that people with active celiac disease had higher-than-average levels of CB1 and CB2 receptors in their intestines. In comparison, celiac patients who had been following a gluten-free diet for 12 months had normal levels.
These results suggest that celiac disease increases activity in the ECS, possibly as a response to increased inflammation. Various studies on the ECS and inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, have shown similar changes.
Cannabinoids such as THC and CBD interact with the ECS to provide a range of benefits. One of these is reducing inflammation, a critical factor in many digestive disorders.
However, the potential for cannabis to help celiac disease does not end there. It may also alleviate a variety of other symptoms associated with CD such as fatigue, nausea, irritability, and depression.
In conclusion: CD is a disorder that affects the small intestine and is characterized by an abnormal immune reaction to gluten-containing foods. Recently, celiac disease has been found to be associated with abnormalities in the endocannabinoid system. Further research is needed to determine whether or not cannabinoids could be used as a potential treatment for CD.
Stay connected for free resources to expand your health and vitality with non-allopathic remedies and natural CBD solutions.
